Tonsillectomy, Adenoidectomy (Tonsil Removal)
Tonsillectomy, Adenoidectomy (Tonsil Removal)
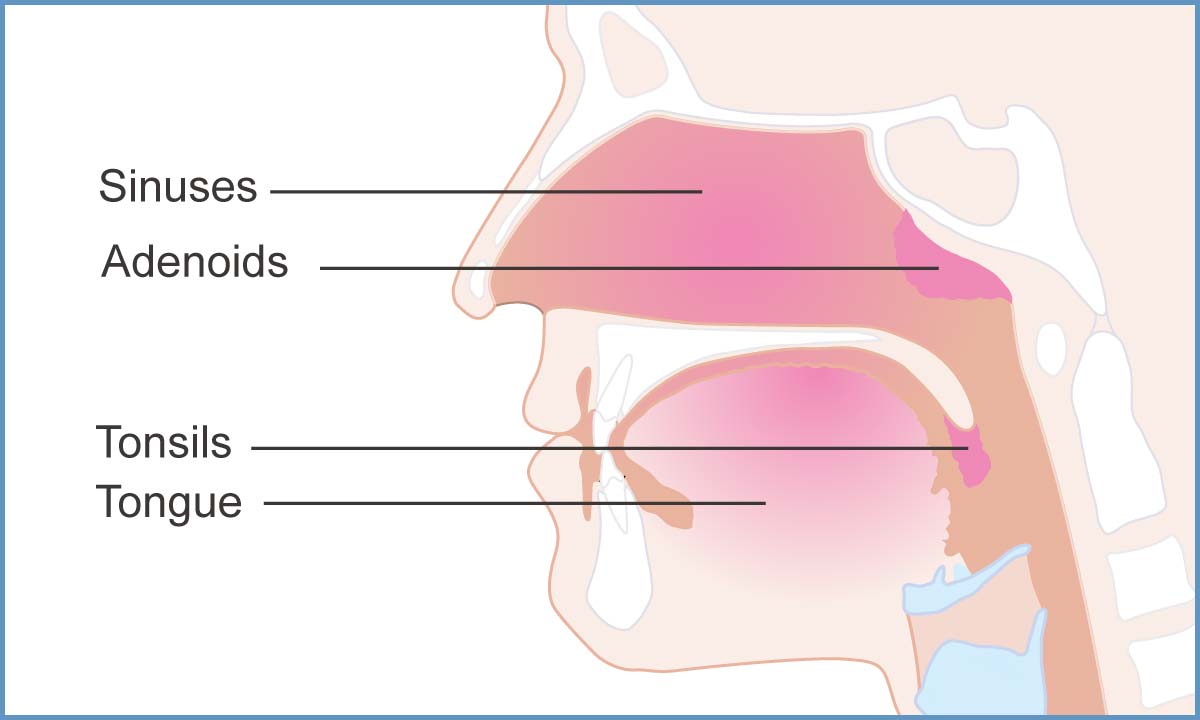
Tonsils are oval-shaped nodes on the sides of the throat, and adenoids are glands at the very back of the roof of the mouth. Both help your body prevent and fight infections as part of your lymphatic system. Tonsils are believed to stop germs from entering your body, and tonsils and adenoids produce antibodies to fight bacteria and viruses. However, they can also become infected themselves, which can lead to other problems. Many older adults may have had their tonsils and even their adenoids removed as children because the procedure was once very routine. Today, neither is performed as often. Removal of the tonsils or adenoids is more likely to become necessary in children than in adults, but both may benefit from the procedures.